Year: 2015
This is Blog #9 of 13 in our Solid State Drives 101 educational series. If you're ready, continue to Blog #10: Wear Leveling. This article follows the Controller Architecture article on NAND Channels and Banks. It will focus on the main blocks of a generic SSD controller and its connection to the NAND flash. Controller functionality varies with...

High reliability Industrial Grade Flash Storage Devices are designed to operate in the harshest environments with the highest write cycles. They also meet the needs of applications which require a locked Bill-Of-Material and long life cycles. A typical flash storage device is designed for cost and/or performance. This is the majority of the marketplace today since consumer...

This is Blog #8 of 13 in our Solid State Drives 101 educational series. If you're ready, continue to Blog #9: Controller Block Diagram. This article follows the Basic SSD Controller Architecture article. It will focus on the connection between the SSD controller and the NAND flash. There are many NAND configurations in SSD design and it makes a...
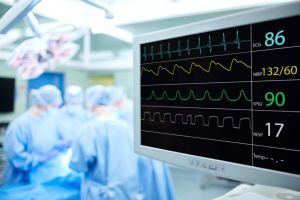
Embedded industrial data storage flash devices have been used in many medical device applications due to their high reliability, modular form factors and long life cycles without BOM change. For many medical devices, a relatively simple memory device like NOR flash and serial flash can meet all the needs of a design. An example would...

Over the years, I've seen many embedded systems designed to a specific vendor's flash card. In most cases, industry standard specs were available at the time of the design as reference. The industry standard specs contain signal and timing information for worst-case situations on a given form factor. Read the rest at: http://embedded-computing.com/guest-blogs/design-your-flash-card-interface-to-the-spec-not-to-a-vendor/

This is Blog #7 of 13 in our Solid State Drives 101 educational series. If you're ready, continue to Blog #8: Channels & Banks. Previous articles described the NAND architecture from the basic NAND cell to a packaged component. This article begins to integrate the controller into the picture. Without a controller, the NAND is a relatively unintelligent...

For simple consumer applications, like replacing a hard drive with a solid state drive in an individual’s notebook computer, limited technical support is required. At most, there may be some questions regarding specifications and installation which can be easily summed up in a brief document. What is a solid state drive used for might be handy. But...

This is Blog #6 of 13 in our Solid State Drives 101 educational series. If you're ready, continue to Blog #7: Basic Controller Overview. Previous articles on the NAND architecture started at the basic NAND cell and built up to the NAND die level. We go up one more level in this article to discuss common NAND component...

Over the past several years there has been a migration from Hard Disk Drives (HDD) to Solid State Drives (SSD). The added SSD advantages of performance, power and environmental specifications have proven to outweigh their additional cost in many applications.The ease of interchangeability of SSD for HDD, has made the switch happen without much thought....
One of the recurring themes when talking to embedded industrial design engineers is how much they hate to reopen an old design to solve an obsolescence issue. Not only is it annoying to redesign something that's working perfectly fine, but in many cases it comes with the added cost of requalification and/or recertification. What is a...






